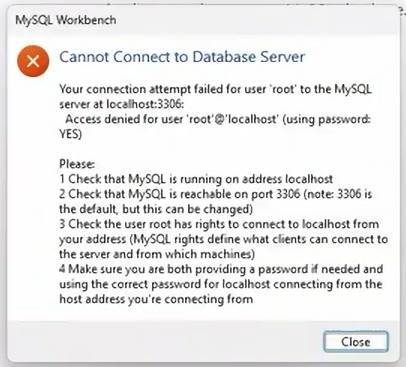
Ever locked yourself out of your own MySQL database? Yeah, me too. It’s frustrating when you’re trying to connect to your local MySQL database server and get that dreaded “Access denied” message because you’ve forgotten the root password. Don’t worry; it happens to the best of us! Resetting the root password is quite simple, and I’m going to walk you through it step-by-step. Let’s get you back into your database!

Step 1: Create an Initialization File
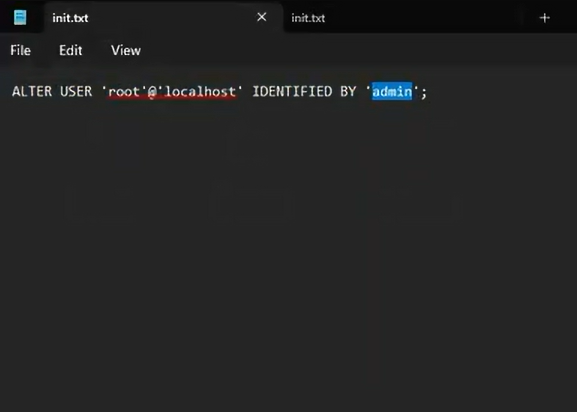
First, we need to create a new file named init.txt. This file will contain the command to reset the root password. You can name it whatever you want, but init.txt is straightforward and easy to remember.
- Create the File: Open your favorite text editor (Notepad, VS Code, Sublime Text, etc.) and create a new file.
- Enter the Reset Password Command: Add the following command to the file. Be sure to include the single quotes exactly as shown.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'admin';In this command, I’m setting the new password to ‘admin’. Feel free to change ‘admin’ to any password you prefer, but remember to keep it secure! - Save the File: Save the file as
init.txt.

Step 2: Move the Initialization File to the C Drive
Now that we have our init.txt file, let’s move it to the C drive. This step isn’t strictly mandatory, but it simplifies the path and makes the next commands easier to manage.
- Copy the File: Copy the
init.txtfile. - Open Explorer: Open Windows Explorer.
- Move to C Drive: Navigate to your C drive and paste the
init.txtfile there.
Step 3: Locate the my.ini File
Next, we need to find the my.ini file. This file contains the configuration settings for your MySQL server. By default, the ProgramData folder is hidden, so we’ll need to make it visible.
- Open Explorer: Open Windows Explorer.
- Show Hidden Items:
- Click on the “View” tab.
- In the “Show/hide” section, check the “Hidden items” box. The
ProgramDatafolder should now be visible.
- Navigate to the MySQL Data Directory: Go to the
ProgramDatafolder, then navigate to the MySQL directory. The path should look something like this:C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0. Note that “8.0” might be a different version number depending on your MySQL installation. - Find
my.ini: Inside the MySQL Server folder, you should see themy.inifile.
Step 4: Construct the Command
Now, we’re going to construct the command that will reset the password using the init.txt file.
- Copy the Path: Copy the path to the directory containing the
my.inifile. You can do this by clicking in the address bar in Windows Explorer and copying the path. - Open Command Prompt as Administrator: Press the Windows key, type
cmd, right-click on “Command Prompt,” and select “Run as administrator.” - Enter the Command: In the Command Prompt window, enter the following command. Replace
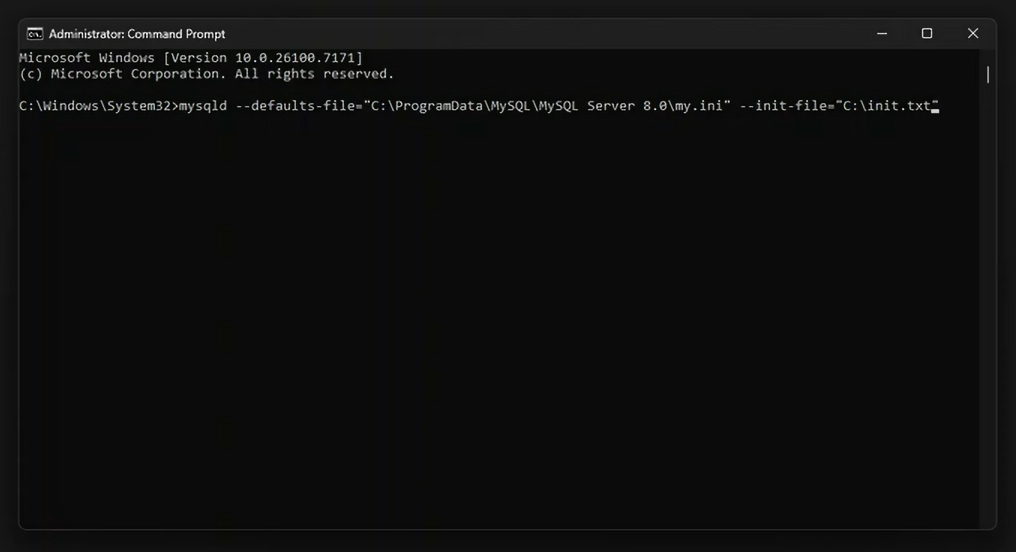
<path_to_my.ini>with the path you copied earlier.mysqld --defaults-file="<path_to_my.ini>\my.ini" --init-file="C:\init.txt"For example, if yourmy.inifile is located inC:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0, the command would be:mysqld --defaults-file="C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\my.ini" --init-file="C:\init.txt"

Step 5: Stop the MySQL Service
Before running the command, you need to stop the current instance of the MySQL service.
- Open Services: Press the Windows key, type
services, and click on “Services.” - Find MySQL Service: Scroll down until you find the MySQL service. It will likely be named something like “MySQL80” (the “80” might be different depending on your version).
- Stop the Service: Right-click on the MySQL service and select “Stop.”
Step 6: Execute the Command
Now that the MySQL service is stopped, you can execute the command to reset the password.
- Run the Command: In the Command Prompt window (the one you opened as administrator), paste the command you constructed in Step 4 and press Enter.
mysqld --defaults-file="C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\my.ini" --init-file="C:\init.txt"This command runs the MySQL daemon (mysqld) with the specified configuration file and initialization file, which contains the password reset command. - Wait for Completion: Give it a minute or two to execute. You might not see any output, but that’s perfectly fine.
Step 7: Log in with the New Password
Now that you’ve executed the command, you can try logging in with the new password.
- Open Command Prompt: Press the Windows key, type
cmd, and hit Enter. - Connect to MySQL: Enter the following command:
mysql -u root -pThis command attempts to connect to the MySQL server as the root user, prompting you for a password. - Enter the New Password: When prompted for the password, enter the password you specified in the
init.txtfile (in my case, ‘admin’). If everything worked correctly, you should be logged in to the MySQL server. You’ll see themysql>prompt.
Step 8: Restart the MySQL Service
Now that you’ve confirmed that you can log in with the new password, it’s time to restart the MySQL service.
- Open Services: Press the Windows key, type
services, and click on “Services.” - Find MySQL Service: Scroll down until you find the MySQL service (e.g., “MySQL80”).
- Start the Service: Right-click on the MySQL service and select “Start.”
Step 9: Connect with MySQL Workbench
Finally, let’s try connecting to the MySQL server using MySQL Workbench.
- Open MySQL Workbench: Launch MySQL Workbench.
- Enter Credentials: Enter the username “root” and the new password you set (e.g., ‘admin’).
- Connect: Click “OK” or “Connect.” If everything went smoothly, you should now be able to connect to your MySQL server in MySQL Workbench with the new password.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes, things don’t go as planned. Here are some common issues you might encounter and how to fix them:
'mysqld' is not recognizedor'mysql' is not recognized: This error means that the command prompt can’t find themysqldormysqlexecutable. To fix this, you need to navigate to the directory where these executables are located and run the commands from there.- Locate the
binDirectory: Find thebindirectory within your MySQL installation directory. The path is usually something likeC:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin. - Open Command Prompt as Administrator: Press the Windows key, type
cmd, right-click on “Command Prompt,” and select “Run as administrator.” - Navigate to the
binDirectory: In the Command Prompt window, use thecdcommand to navigate to thebindirectory. For example:cd C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin - Run the Commands: Now, run the
mysqldcommand from this directory.mysqld --defaults-file="C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\my.ini" --init-file="C:\init.txt"
- Locate the
Path not found: Double-check the paths in your commands to ensure they are correct. A simple typo can cause this error. Make sure themy.inifile andinit.txtfile are located at the paths you specified.- Service fails to start: If the MySQL service fails to start after resetting the password, check the MySQL error log for any clues. The error log is typically located in the MySQL data directory.
Key Takeaways
- Resetting the root password in MySQL is straightforward but requires careful attention to detail.
- Creating an initialization file with the password reset command is the first step.
- Stopping the MySQL service before running the reset command is crucial.
- If you encounter errors, double-check your paths and ensure you’re running commands from the correct directory.
- Always remember to restart the MySQL service after resetting the password.
FAQ Section
Q: What if I forget the new password I set?
A: You’ll need to repeat the password reset process from the beginning. Keep your passwords in a secure place!
Q: Can I use a more complex password in the init.txt file?
A: Yes, you can use a more complex password. Just make sure to enclose it in single quotes.
Q: Does this method work for all versions of MySQL?
A: This method should work for most versions of MySQL, but the exact steps might vary slightly depending on your version.
Q: Do I need to move the init.txt file to the C drive?
A: No, moving the init.txt file to the C drive isn’t mandatory. It just simplifies the path and makes the commands easier to manage. You can keep it anywhere, but make sure to use the correct path in the command.
Q: What if I don’t have the ProgramData folder?
A: The ProgramData folder is hidden by default. You need to enable “Show hidden items” in Windows Explorer to see it.
Q: Can I reset other user passwords using this method?
A: Yes, you can modify the SQL command in the init.txt file to reset the password for any user. Just change the username in the ALTER USER command.
Conclusion
Resetting your MySQL root password might seem daunting, but by following these steps, you can quickly regain access to your database. Remember to pay close attention to the paths and commands, and don’t hesitate to troubleshoot if you encounter any issues. I hope this guide has been helpful, and now you get back to building cool stuff!
